Swift Memory Layout
Swift Memory Layout
Unsafe Pointer
在开始介绍Memory Layout之前,先介绍下Swift指针。如图所示,除了黑色Unsafe和Pointer固定外,其他都是可选的,一共有8种不同的类型。

Memory Layout
早在Swift3.0的时候就推出函数MemoryLayout计算内存大小。其中分为如下3个参数
MemoryLayout<T>.size //内存大小
MemoryLayout<T>.stride //分配的内存大小
MemoryLayout<T>.alignment //内存对齐大小
比如:
MemoryLayout<Int32>.size //4
MemoryLayout<Int32>.stride //4
MemoryLayout<Int32>.alignment //4
size
**MemoryLayout
除了计算基础类型外,也可以计算结构体和对象
struct Person {
let age:Int64
let sex:Bool
}
MemoryLayout<Person>.size // 9
MemoryLayout<Person>.stride //16
MemoryLayout<Person>.alignment //8
stride & alignment
什么是内存对齐
CPU 更高效地读写内存,采用了word size读取方式,避免造成额外的开销;但是也要求类型的存储地址要与其内存对齐。
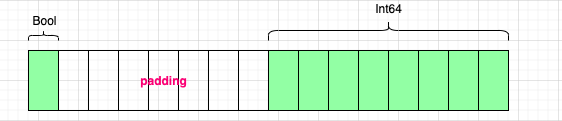
我们修改下上面的demo如下:为什么修改了下属性的顺序,结构体的size变化了呢?
struct Person {
let sex:Bool
let age:Int64
}
MemoryLayout<Person>.size // 16
MemoryLayout<Person>.stride // 16
MemoryLayout<Person>.alignment // 8
首先我们分别获取属性Bool和Int64的内存模型
MemoryLayout<Bool>.size //1
MemoryLayout<Bool>.stride //1
MemoryLayout<Bool>.alignment //1
MemoryLayout<Int64>.size //8
MemoryLayout<Int64>.stride //8
MemoryLayout<Int64>.alignment //8
- 首先是Bool类型,内存对齐是1,当前内存对象是1的倍数不需要padding,所以第一个字节是赋值Bool
- 第2个属性是Int64,内存对齐是8,当前内存地址是1,不是8的倍数,需要padding7个字节
- 地址8-16是Int64赋值,所以MemoryLayout
.size = 16 - MemoryLayout
.alignment = Max( MemoryLayout .alignment ,MemoryLayout .alignment ) = 8 - Person.alignment 满足8字节的内存对齐,不需要再padding,所以MemoryLayout
.stride = 16
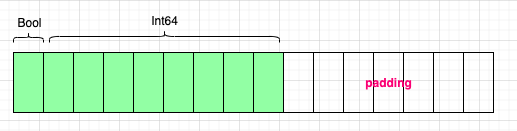
请画出:未交换属性之前的内存图
实战
在xcode中,去真正内存中看下是否满足我们的猜想
-
初始化一个结构体
var person = Person(sex: true, age: 11),打印结构体地址withUnsafeMutablePointer(to: &self)或者通过如下方式
-
查看该地址在内存的信息

第一个字节是01 表示 let sex:Bool ,然后padding7个0x00 字节,最后0x000000000000000B 表示 11,就是我们设置的 let age:Int64
猜想
从结构体的内存模型来看,好像无法区分是什么类型,如果我定义一个一摸一样的结构体,是不是可以偷天换日呢?
struct Person {
let sex:Bool
let age:Int64
}
struct Person2 {
let sex:Bool
let age:Int64
}
var person = Person(sex: true, age: 11)
let rawPointer = UnsafeMutableRawPointer.allocate(byteCount:MemoryLayout<Person2>.stride, alignment: MemoryLayout<Person2>.alignment)
let personPointer = withUnsafeMutablePointer(to: &person) {
return UnsafeMutableRawPointer($0).bindMemory(to: Int8.self, capacity: MemoryLayout<Self>.stride)
}
rawPointer.copyMemory(from: personPointer, byteCount: MemoryLayout<Person2>.stride)
let person2 = rawPointer.load(as: Person2.self)
XCTAssertTrue(person.sex == person2.sex && person.age == person2.age)
//pass
总结
-
MemoryLayout
.alignment = Max( MemoryLayout .alignment ,MemoryLayout .alignment ) -
MemoryLayout
.size = MemoryLayout .size + padding + ... + MemoryLayout .size -
MemoryLayout
.stride = MemoryLayout .size + padding 其中padding是通过内存对其来计算的